CTF Tips
by kpax
Initial Setup
When participating in a HTB CTF, you will get questions based on the following topics
- Reversing (Using reverse engineering tools, such as Ghidra, GDB, Pwntools, etc)
- Crypto (Breaking Cryptography)
- Coding (Writing code to solve challenges)
- Web (Website attacks)
- Forensics (Investigation into evidence left behind by simulated attacks)
- Pwn (Attempting to retrieve the flag using multiple techniques)
Dealing with Python modules
Installing a virtual environment
On newer versions of Kali and ParrotOS, the python ecosystem for the Operating System is locked down, to avoid breaking packages that relay on certain versions of Python Modules.
When attempting CTFs, it is quite often necessary to install python modules that conflict with the Operating System versions.
We can get around this by installing a Python Virtual Environment
The command for this is as follows
python -m venv <Name of Virtual Environment>
Example : python -m venv venv
Running the command above will create a Python Virtual Environment in a directory called venv in your current working directory.
Activating the Environment
To start using your new Python Virtual Environment run the following command (Notice the dot at the beginning)
. venv/bin/activate
Your shell prompt will change to be prefaced with the name of the Virtual Environment you specified. In this case, venv
Using the Environment
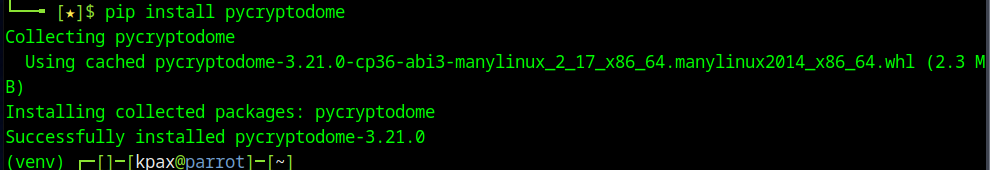
Now you are in a Python Virtual Environment, any python commands you run will work with that environment. If you use pip to install a module, then the module will be installed under the venv folder structure
If a python script has a hashbang of #!/usr/bin/python3 and you make it executable, then running the script with .\<script name> will not use your Python Virtual Environment.
When running a python script within a Python Virtual Environment, make sure to run it using python3 <script name>, rather than .\<script name>
Deactivating the Environment
To stop using the Python Virtual Environment, simply run the command deactivate and you will go back to python commands using the Operating System libraries.
GDB basics
I am by no means an expert in GDB, but these are some basic commands I have found useful
si # Move to next instruction
x /s *$rdi # View the string stored at the RDI register
b main # Break at the main part of the program
b *0xffffff34f4 # Break the execution at memory address 0xffffff34f4
c # Continue execution until next breakpoint